What is an Internet Domain Name
Internet Domain Name
What is an Internet Domain Name
Internet domain name is the unique and unrepeatable name that is given to a site on Internet so that the brands, organizations or persons who own such sites can be identified in a comfortable and simple way by the users. Internet domain names link a physical address of an Internet server (IP address) to a web site, so they are memorable terms and easy to remember by users.
Internet domain names are exclusive they belong to a single owner, for this reason there are different Internet domain name providers that are in charge of managing them. These domain name providers are regulated by ICANN.
The structure of domain names is composed by the customized domain name associated with the brand or business and the domain extension. The different extensions that an Internet domain name can have are described below.
Internet domain extensions
Internet domain name extensions indicate the level of the domain in question: top-level domain (TLD), second-level domain (SLD) or if it is a subdomain. Domain name extensions correspond to the character strings to the right of the dot next to the custom domain name.

Top Level Domain (TLD)
TLD are the main domain name extensions, generally corresponding to the string of characters to the right of the last dot in the domain name.
TLD Types
- gTLD: generic top-level domain
- sTLD: sponsored top-level domain
- ccTLD: country code top-level domain
gTLDs are the most common type of top-level domain that do not have any registration restrictions. Some examples of gTLDs are:
- .com
- .org
- .net
Ideally, each gTLD type should represent the purpose of the web site. For example, .com should be used for commercial sites, while .org should be reserved for organizations only.
sTLDs are managed by private organizations. This means that it is only possible to register a sTLD if you follow specific rules and have certain permissions to do so.
Examples of sTLDs include:
- .gov: for government institutions only
- .edu: for educational institutions
- .mil: for military organizations
The last type of top-level domain is the ccTLD. This represents the geographic location or country in which the website or organization is located.
Examples of ccTLDs include:
- .us: USA
- .mx: Mexico
- .es: Spain
Second Level Domain (SLD)
A second level domain is below the TLDs in the domain name hierarchy. It is the string of characters preceding the TLD extension, located to the left of the last dot, for example, in mydomain.ac.com, the SLD would be ac.
Some domain name providers use a second-level domain to indicate that a specific entity is registered.
Subdomain
A subdomain indicates a separate division of a main domain that shares the same servers and the same main domain name. It is not necessary to register a subdomain. The most common reason for creating subdomains is to organize and divide website contents into diferent sections. For example, to separate the blog or online store from the main website.
The custom domain name and its extension integrate the website URL, however, it is important to note that they are not the same element.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
Although a domain name and a URL share some similarities, they refer to different elements. An URL is a complete website address that can redirect users to a specific page within a website. A domain name is only part of the URL. Every piece of content on the Internet, regardless of its format or purpose, has a specific URL that indicates where it is hosted.
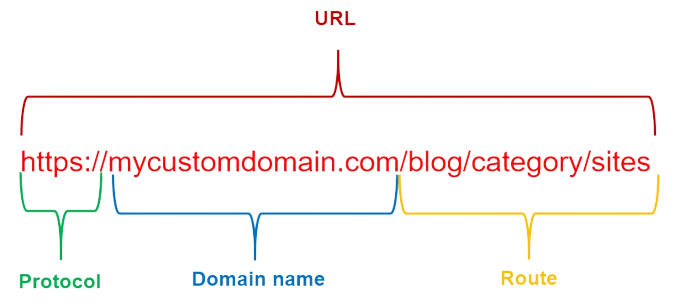
An URL is composed by a protocol, a domain name and an online route. The protocol shows if the website has a SSL certificate. URLs have an internet route only when they redirect users to a specific page within a website.
Conclusions
Domain names are customizable so they usually reflect the nature of the website and their extension should denote its geographic scope. The domain name should not be confused with the URL of the website on Internet. It is important to properly select the domain name of the business or website you wish to publish because this will facilitate its location and access by users or potential clients.
Acquiring a domain name is the first step that any company wishing to position itself on Internet must take. The acquisition of a domain name is done by contracting it from Internet domain name providers.